Worms in humans cause the development of diseases collectively called helminthiasis. Worms are parasitic worms that can be found in almost all organs of our body: intestines, muscles, lungs, liver, heart and even eyes.
If a person has worms, symptoms do not always appear; if they do occur, they are disguised as other diseases of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, etc. Sometimes these symptoms are so vague that it can be very problematic to establish the cause of a particular problem, especially when it comes to children.
Today, there are many known parasites that can infect the human body. In total there are about 150 types of helminthiasis. All worms, according to their shape and body structure, are divided into two large groups: roundworms or nematodes, and flatworms.
Children are most often infected with worms, and the most common forms of helminthiasis (diseases caused by parasitic worms) are ascariasis and enterobiasis. The most dangerous worms that can live in the human body are echinococcus and alveococcus. For each group of parasites, special means have been developed, treatment of which will remove worms from the body of an adult or child.
Types of worms in humans
There are more than two hundred species of worms that infect humans. Most of them are not found in the middle zone, so about sixty species are common in our country. Parasites are divided into contact parasites (worms transmitted from one person to another), geohelminthiasis (the larva lives in the soil, and invasion occurs when soil particles enter with food) and biohelminthiasis (parasites pass into the human body through the meat of infected animals or fish).
Let's name some of the most common groups of worms in humans:
- Annelids - pinworms, roundworms, whipworms, trichinella;
- Tapeworms – various types of tapeworms, echinococci, tapeworms;
- Flatworms - all kinds of flukes, flukes.
Let's take a closer look at each type of worm that can live in the body of an adult.
- Roundworms are large roundworms, red-yellow in color, reaching a length of up to 40 cm in adulthood.
- The whipworm is a round worm 30-50 mm long, which got its name because of the shape of its body: the front part is long and narrow, like a hair, and the back part is short and wide.
- The broad tapeworm is a large tapeworm reaching a length of about 10 meters; individuals over 20 meters in length can be found.
- Hookworm is the combined name for two types of worms: duodenal hookworm, and necator, roundworms 10-15 mm long.
- Trichinella are small roundworms 2-5 mm long that cause a serious disease - trichinosis.
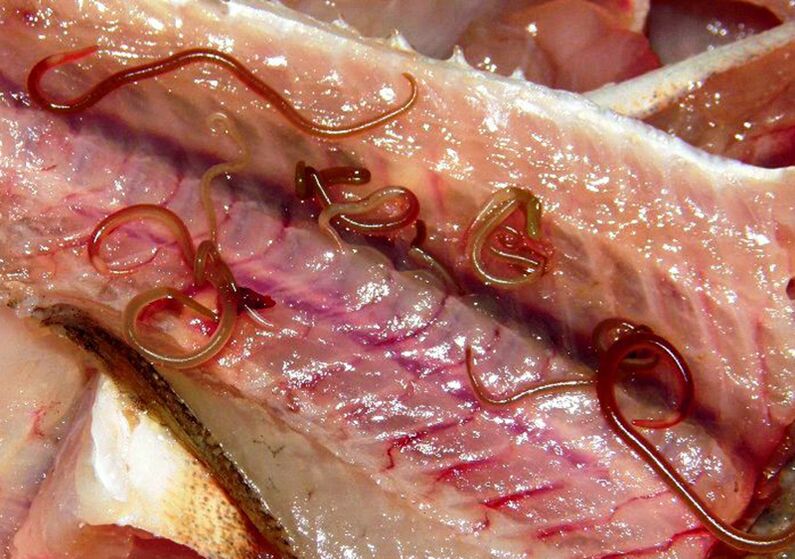
- The liver fluke (cat fluke) is a flatworm from the class of flukes 7-20 mm long. The disease caused by this parasite is called opisthorchiasis.
- Pork and bovine tapeworms are similar in structure tapeworms up to 6 meters long.
- Echinococcus parasitizes the human body not in adult form, but in the form of an intermediate form - Finns. Echinococcus itself is a tapeworm 3-5 mm long
- Alveococcus is a worm similar to echinococcus, with a similar structure and development mechanism.
Symptoms and signs of worm infestation depend on the type of parasite, its location in the body, and the stage of its development.
Helminths in the human body
Worms are scientifically called helminths. Helminths mean any worms that parasitize the bodies of people, animals, and plants. Accordingly, helminths are not a specific type of parasite, but a whole group of different worms, three of which are the most common.
In modern society, helminths are still widespread. Especially often, helminthic infestation occurs in children, hunters, fishermen and their families, as well as rural residents.
Helminths are a large order of parasitic worms that live off animals and plants, feeding and reproducing inside the donor’s body. Man is no exception. In our country alone there are more than 70 species of parasites. According to statistics, every third inhabitant of the Earth is infected with parasitic worms. It is assumed that there is not a single adult person during whose lifetime not a single worm has settled in his body.
Helminths. No matter how carefully parents monitor the cleanliness of their children’s hands, it is almost impossible to protect them from worms (pinworms). Children explore the outside world; nature awakens a special interest. They want to touch everything with their hands and taste it. People who eat fish, meat of wild animals and birds, and homemade milk are at risk of becoming infected with trichinosis and diphyllobothriasis.
Modern medical data show that many diseases occur due to helminthic infestation. For example, the connection between oncology and long-term infection with parasites has been clinically proven. Signs of the presence of worms in humans are often misinterpreted by doctors and patients. They begin to treat non-existent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How can you get infected?
The causes of human worm infection are very diverse, the route of infection directly depends on the type of worms and their life cycle, it can be:
- eating dirty vegetables;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules when preparing food;
- poor heat treatment of some food products, especially animal meat and fish;
- communication with pets – cats, dogs, some types of rodents;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules before eating, after visiting the bathroom, upon returning from a walk;
- swimming in contaminated bodies of water.
During their life, worms produce toxic substances that are absorbed into the blood and spread throughout the body, causing harm to the most important organs and systems.
General symptoms and signs of helminthic infestation in children
General symptoms of helminthiasis include:
- worsening or increased appetite;
- nausea, possibly vomiting;
- excessive salivation;
- stool disorders;
- the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen;
- dizziness, headaches;
- allergic reactions;
- increased frequency of colds;
- irritability, moodiness;
- sleep disturbance;
- deterioration of mental and physical activity;
- dry cough.
Symptoms of worms in humans
Sometimes worms are able to parasitize the body of an adult for a long time without noticeable symptoms; in some cases, they become the cause of the development of various chronic diseases, causing dangerous complications and even death.
With the onset of an acute period of helminthiasis, worms begin to feed intensively in the intestines of a sick person, causing various signs of digestive system disorders: dysbacteriosis, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
Let's see what signs of helminths can be noted? Let us list the most common, general symptoms of worms in humans.
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction - diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain;
- Pain in joints and muscles - parasites can move throughout the human body in order to settle in the most convenient places for their life, for example, in the joint fluid and muscles. When this happens, the person experiences painful sensations;
- Nervous system disorders and general malaise - manifests itself in the form of fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbances and memory problems;
- Allergic reactions and skin manifestations - the appearance of pimples, blackheads and other rashes - are also signs of the presence of worms in humans;
- Decreased immunity and, as a consequence, the development of infectious diseases;
- A sharp decrease in body weight;
- Anemia - some worms suck blood from the intestinal walls like leeches;
- Grinding of teeth during sleep and sleep disturbance;
- Itching in the anus, especially at night. At this time, the female is actively laying eggs, thereby causing itching in the anus;
- Enlarged lymph nodes, low-grade body temperature;
- Inflammation of the respiratory tract - cough, fever, sputum production, runny nose - this is how the presence of worms can manifest itself.
The specific first signs will directly depend on the pathogen and the location of the worm in the human body. For example, large worms, flukes and tapeworms like to parasitize the liver, this can lead to degeneration of liver cells, blockage of the bile ducts, blood clots, and cirrhosis. Roundworms and pinworms live in the intestines, so they will be excreted along with the feces. To find out how to remove these worms from a person, you should consult a doctor, he will prescribe a suitable remedy.
Symptoms of worm infection may appear at different times from the moment of worm infection. So, the first symptoms of ascariasis appear after 2-3 days. With most of all other helminthic infestations, symptoms of the disease appear after 2-3 weeks.
Most often, the main signs of worm infection in an adult are represented by allergic manifestations in the form of itching and rash, swelling, weakness, muscle pain, headache, fever, muscle and joint pain, an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood, etc.
Being parasites, worms feed on the body of their host. At the same time, they absorb a significant amount of proteins and carbohydrates, mineral elements, vitamins and other nutrients. Helminthiases can be acute and chronic. The first last 2-3 weeks and often manifest as allergies, while the chronic stage can last for months, years and even decades.
What organs can worms affect?
There are two types of invasions: cavitary and tissue. Depending on the species, habitats are also divided:
- Cavity worms settle in the small and large intestines. In particular, the first sections of the small intestine are affected by tapeworm, hookworm, and roundworms. The lower part of the small intestine is the habitat of the dwarf tapeworm and pinworm. The large intestine most often becomes the habitat of the whipworm.
- Tissue helminths affect organs of any type: liver, brain, lymph nodes, bile ducts.
Important! It is impossible to determine signs of the presence of worms in a patient at the initial stage of development of the infestation. As long as the number of worms is small, toxic poisoning by waste products is within normal limits, the body itself copes with the invasion. The appearance of characteristic or acute symptoms indicates a significant increase in the number of helminthic infestations: the maturation of individuals and their dynamic development.
Complications of worms
A number of helminths can cause serious disturbances in the patient's condition. Here are the most common complications:
- B12-deficiency anemia, iron deficiency anemia - leads to disruption of oxygen supply to tissues, requiring long-term recovery. Manifested by pale skin, dry mouth, weakness, disturbances in various body functions;
- Intestinal obstruction occurs when the parasite blocks the lumen with its body. Surgical treatment is required. Symptoms – abdominal pain, lack of stool, vomiting;
- Intestinal bleeding - if the worm attaches to the intestinal wall, it can damage its blood vessels. Symptoms: abdominal pain, weakness, blood in the stool, vomiting. Requires surgical treatment;
- Fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver develops with a long course of opisthorchiasis. The changes are irreversible. Symptoms: disruption of sleep and wakefulness, accumulation of fluids in body cavities, loss of liver function;
- Abscesses of the affected organs are purulent inflammations. Symptoms are pain, high fever, weakness. The condition is rapidly deteriorating. An examination is required to detect the source of inflammation and surgical treatment.
Stool analysis and scraping for worm eggs
Worms are primarily intestinal parasites. It is through the intestines that their eggs are released. Therefore, to diagnose them, feces are taken for analysis. You can purchase a special container for collecting stool at the pharmacy, although you can also use a matchbox or jar.
So, to take the analysis you will need a container for collecting material and a spatula. If a person sees fragments of worms or a whole helminth, then he also needs to be sent to the laboratory.
It is not necessary to take stool to the laboratory immediately after collection. It must be delivered for examination within 24 hours. Until then, the collected biomaterial should be stored in the refrigerator. An exception is the collection of stool for testing for giardiasis. It must be handed in warm, since the parasite cysts are destroyed when cooled. While the stool is being delivered to the laboratory, the container should be wrapped in a warm cloth.
To diagnose enterobiasis, a scraping is taken from the perianal folds, since female pinworms lay eggs in this area. Before the test, you should not wash your face for about 12 hours or visit the toilet. Therefore, the optimal time to perform analysis is in the morning.
Scraping is performed using a cotton swab, which is placed in a clean container and delivered to the laboratory. You can also use adhesive tape, which is peeled off the glass, attached to the anal area for a while, then torn off and returned with the sticky side to the glass.
Biological material delivered to the laboratory is studied using a microscope. If a person is infected, the laboratory technician will see worm eggs, their larvae or segments. Each parasite lays eggs that are unique to its species. Therefore, by studying the structure of the egg, you can determine which worm is parasitic in the human body.
If there is a worm in the feces, then most often it looks like a white strip of varying lengths. Worms can remain mobile. The type of worm can be determined in the laboratory.
However, it is not always possible to detect worms using stool analysis. For example, the analysis will be uninformative if the human body is parasitized only by male roundworms that cannot secrete eggs.
Blood test for worms
To identify worms in the blood, an immunological test is used to determine antibodies to the main types of helminths. The reliability and accuracy of ELISA is equal to 95%. It can be used to detect extraintestinal forms of helminthiases.
Decoding of ELISA results in a simplified form:
- Helminths parasitize the body if immunoglobulin class M (lgM) is elevated in the blood.
- Worms were either present in the human body before, or the helminthic infestation became chronic and caused a weakening of the human immune system. This conclusion can be made if the level of IgG immunoglobulins is elevated, but lgM is not detected in the blood.
In both cases, more in-depth diagnosis and specific treatment will be required.
How does the parasite become infected and develop?
Each parasite has specific life cycle characteristics. Depending on the mechanism of infection, all helminthiases are divided into three main groups:
- contact helminthiases;
- geohelminthiases;
- biohelminthiases.
Contact helminthiases
The development of parasites included in the group of contact helminth infections occurs entirely in the child’s body. Worm eggs enter the digestive system, migrate to the intestines and after some time turn into adults. Sexually mature helminths form eggs, which are released with feces into the external environment. The development cycle repeats itself again.
Contact helminthiases include pinworm infection. The spread of these worms occurs through the fecal-oral mechanism. If a child does not wash his hands after using the toilet, then microscopic pinworm eggs remain on his fingers. Other children can become infected through contaminated household items and food that the sick person has touched. In the spread of pinworms, non-compliance with personal hygiene rules is of great importance. Therefore, this helminthiasis is more common in childhood.
In addition to infecting others, a sick child can reinfect himself. Pinworms crawling out of the anus lay eggs on the skin in the anal area. This process causes severe skin itching, so children often begin to scratch the sore spot. If they do not wash their hands after this, then a new portion of eggs penetrates the intestines. The parasite population increases, which leads to a deterioration in the child’s condition.
Geohelminthiasis
The group of geohelminthiasis is represented by roundworms. For these parasites to develop, it is necessary for the feces of a sick child to enter the ground. The released eggs begin to actively develop and quickly reach the invasive stage, at which they can penetrate the human body.
Infection of children usually occurs through the consumption of unwashed vegetables and fruits that come into contact with the ground. Ascaris larvae remain on them, which penetrate the child’s intestines and cause unpleasant symptoms of helminthiasis.
Biohelminthoses
For the development of worms belonging to the group of biohelminths, the presence of an intermediate host is necessary - a living organism in which the worm larvae will develop. This can be cattle (cows, pigs), as well as fish. Therefore, a child can become infected with worms by consuming foods from unverified sources. Insufficient heat treatment of meat or fish contributes to infection. Through food you can become infected with echinococcus, bovine and pork tapeworm, and cat fluke.
Treatment of worms in humans
The basis for the treatment of worms in humans are specific anthelmintic drugs; adults are prescribed the best time-tested tablets.
The choice of drug for treatment depends on the presence of specific worms in the human body. In the acute period of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the patient antiallergic drugs, such as Suprastin or Claritin.
Only on the basis of tests and diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment for worms in a person, since antihelminthic drugs are quite toxic. If, during the analysis, worms are detected again, then the specialist determines how to remove the worms, proposing a new treatment regimen based on the use of other anti-worm tablets that will better cope with the task.
Treatment
Anthelminthic therapy
The basis for the treatment of parasitic diseases are anthelmintic drugs. They must be usedstrictly as prescribed by the doctor, since when selecting a drug it is necessary to take into account a number of important factors:
- form of helminthiasis;
- phase of disease development;
- pathogen;
- concomitant diseases of the child;
- features of his condition.
Only a doctor can correctly assess these indicators and select the optimal drug. Self-medication for helminthiasis in children is unacceptable. Incorrectly chosen therapy is often not only ineffective, but also accompanied by severe side effects.
How to take a stool test for helminths and their eggs?
When selecting therapy, the doctor must take into account the causative agent of the disease. You should not rely on a universal remedy, since most drugs act only on a certain circle of helminths. If the wrong drug is used, the clinical picture of the disease in the child does not disappear, the disease continues to progress, which can lead to serious complications.
If there are several children in a family, doctors often recommend anthelmintic therapy for all family members at once. This will prevent repeated cases of helminth infection after treatment.
Symptomatic therapy
In addition to anthelmintic therapy, the child is also prescribed symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating the clinical manifestations of the disease. If a severe allergic reaction occurs, antihistamines are used - Suprastin, Tavegil, Claritin.
If the baby has severe manifestations of intoxication, he is prescribed antipyretics and painkillers. To relieve acute symptoms, plenty of fluids are prescribed or infusion therapy is performed. If there is a risk of developing vasculitis and myocarditis, glucocorticoids (for example, Prednisolone) are prescribed.
How to treat worms with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment include medicinal plants that have anthelmintic and laxative effects. Although the effectiveness of these remedies has not been scientifically tested, many of them have been used since ancient times to treat intestinal worms in humans at home.
- The best folk remedy is pumpkin seeds for worms. Take and peel pumpkin seeds (80-100g), try not to damage the green skin. Grind them, add 2 tablespoons of honey and 100 grams of water, mix. This remedy must be taken strictly in the morning, on an empty stomach. One dining boat every hour for 3 hours. Afterwards you need to take a laxative, and after 1-2 hours give an enema.
- Pomegranate. Pomegranate bark contains punicin, which is highly toxic to worms. A decoction of the bark in fresh water should be taken three times a day by adults and children suffering from parasites.
- Onion broth (pour 200 ml of boiling water over 1 onion, leave for 2 days, consume before meals for 4 days)
As for prevention, to prevent helminthic infestation, it is necessary to wash your hands with soap after returning from the street, heat treat meat and fish, do not drink raw water and do not swim in polluted water bodies.
Prevention
The main prevention of helminthiasis in children is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
Therefore, we can name precautionary measures to prevent helminthic infestations:
- instilling personal hygiene skills in children (washing hands after visiting the toilet, contacting animals, walking outside, before eating);
- fighting bad habits (the child should be prohibited from sucking fingers, biting nails, or putting foreign objects in his mouth);
- control of mosquitoes, flies and insects;
- high-quality processing of meat and fish;
- high-quality water disinfection;
- deworming of domestic dogs and cats;
- avoid contact with stray animals;
- thorough washing of greens and vegetables, berries and fruits;
- frequent change of underwear and bed linen (once a day);
- ironing underwear and bed linen with a hot iron;
- performing hygiene procedures in the anal area twice a day to prevent enterobiasis;
- wearing panties with elastic bands at night;
- thorough wet cleaning of premises.
Once in the body, helminths in children disrupt the normal functioning of various organs and systems. And if adults have a strong immune system constantly fighting against "uninvited guests, " then this does not happen in a child: his body is still weak and vulnerable. Therefore, it is important to teach the child to observe personal hygiene standards as early as possible to prevent helminthic infection, and if symptoms appear, immediately contact a specialist for subsequent anthelmintic treatment.